Table of Contents
- What is Java? Understanding the Basics
- Is Java Good for Kids? Pros and Cons
- What Age Should Kids Start Learning Java?
- Java vs Other Programming Languages for Kids
- Essential Java Concepts Kids Need to Know
- Best Resources to Learn Java for Kids
- How to Set Up Java for Kids (Simple Steps)
- 9 Fun Java Projects for Kids to Build
- Java Programming Classes for Kids
- Tips for Parents Supporting Young Java Learners
- Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Java Career Opportunities Kids Should Know About
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, powering everything from Android apps to enterprise software.
But is it suitable for kids? Absolutely! While Java might seem complex at first, it's actually an excellent language for young learners who are ready to move beyond visual programming.
This guide will show you everything you need to know about teaching Java to kids. We'll cover the right age to start, why Java is valuable, how it compares to other languages, and the best resources to begin learning.
Whether your child wants to build games, create Android apps, or develop strong programming fundamentals, Java provides a solid foundation.
What is Java? Understanding the Basics
Java is a powerful, versatile programming language created by Sun Microsystems in 1995 (now owned by Oracle).
It's designed with a "write once, run anywhere" philosophy, meaning programs written in Java can run on any device that has the Java Virtual Machine installed.
Where Java is used:
- Android apps: Most Android applications are built with Java
- Games: Minecraft Java Edition runs on Java
- Web applications: Many websites use Java on the server side
- Enterprise software: Banks, hospitals, and large companies rely on Java
What makes Java different:
Java is an object-oriented programming language, which means it organizes code around "objects" that represent real-world things.
Think of it like building with LEGO sets—you create individual pieces (objects) that work together to build something bigger.
Important clarification: Java and JavaScript are completely different languages despite similar names.
Java is used for applications and Android development, while JavaScript makes websites interactive. Don't let the names confuse you!
Is Java Good for Kids? Pros and Cons
Advantages of Java for Young Learners
Strong foundation in computer science: Java teaches programming concepts that transfer to other languages. Understanding Java means understanding how many professional applications are built.
Industry relevance: Java consistently ranks among the top three programming languages worldwide. Learning Java prepares kids for real-world software development.
Academic preparation: The AP Computer Science A course teaches Java. Kids who learn Java early have a significant advantage in high school and college computer science courses.
Structured learning: Java's strong typing system (specifying what kind of data each variable holds) teaches precision and attention to detail. These are valuable programming habits.
Career opportunities: Software developers who know Java earn competitive salaries, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics reporting median wages above $100,000 for experienced developers.
Challenges to Consider
Steeper learning curve: Java requires understanding more syntax rules than Python or visual languages like Scratch. Kids need patience and persistence.
More verbose code: Java programs require more lines of code to accomplish tasks compared to Python. This can feel tedious for beginners.
Setup complexity: Installing the Java Development Kit and configuring an IDE can be technical. Parents might need to help with initial setup.
Abstract concepts: Object-oriented programming introduces concepts like classes and inheritance that can be challenging without proper explanation.
When Java is the Right Choice
Java works best for kids aged 11 and up who have some prior coding experience. If your child has completed Scratch projects or learned basic Python, they're likely ready for Java.
Consider Java if your child wants to build Android apps, create games beyond visual platforms, or prepare for advanced computer science courses.
What Age Should Kids Start Learning Java?
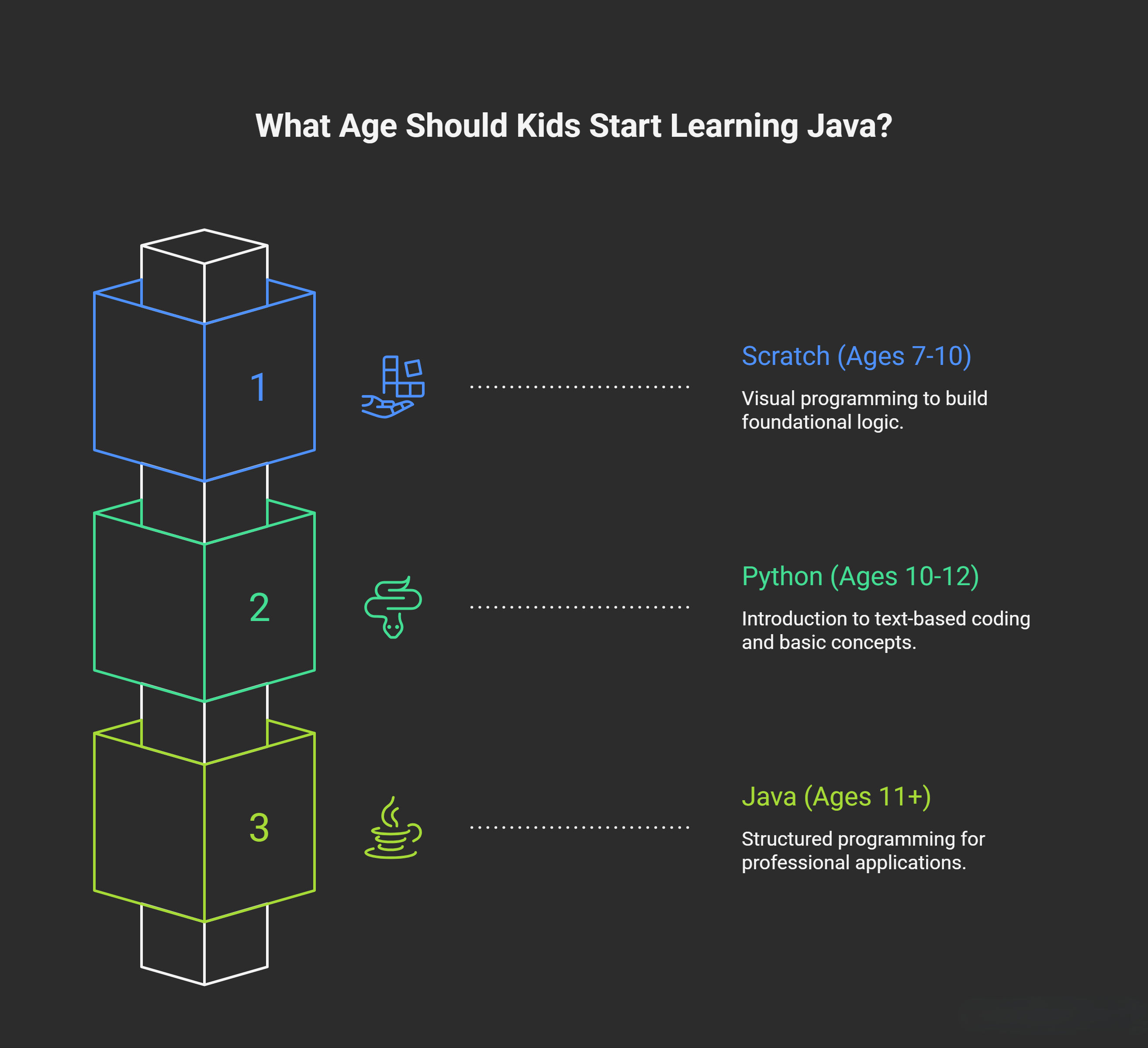
Recommended starting age: 11-13 years old
This age range works well because kids have developed the logical thinking and patience needed for Java's structured approach. They can handle abstract concepts and follow detailed syntax rules.
Prerequisites before starting Java:
- Understanding of basic programming concepts (sequences, loops, conditionals)
- Comfort with reading and following detailed instructions
- Basic math skills (variables, simple equations)
- Experience with at least one programming language or platform
Signs your child is ready:
Your child can explain what a loop does and when to use it. They've completed several programming projects in Scratch or Python. They show interest in building more complex applications. They don't get discouraged by syntax errors.
Recommended learning path:
Start with Scratch (ages 7-10) to learn programming logic visually. Move to Python (ages 10-12) for introductory text-based coding. Then transition to Java (ages 11+) for structured, professional programming.
Java vs Other Programming Languages for Kids
Java vs Python For Kids
Syntax complexity: Python uses simple, readable syntax that feels like writing instructions in plain English. Java requires more formal structure with brackets, semicolons, and explicit type declarations.
Read: Python For Kids
Example comparison:
Python: print("Hello World") Java: System.out.println("Hello World");
When to choose Python first: If your child is new to text-based programming, start with Python. Its simplicity builds confidence before tackling Java's stricter syntax.
When to choose Java: If your child wants to build Android apps, prepare for AP Computer Science, or learn professional development practices from the start.
Many kids learn Python first, then transition to Java once they're comfortable with programming fundamentals. This progression makes Java feel more approachable.
Java vs JavaScript For Kids
Despite similar names, these are completely different languages with different purposes. Java builds applications, games, and Android apps. JavaScript makes websites interactive and runs in web browsers.
Choose Java if your child wants to create software and mobile apps. Choose JavaScript if they're interested in web development and creating interactive websites.
Java vs C++ For kids
Both Java and C++ are statically typed, compiled languages used for professional software development. Java is more beginner-friendly because it handles memory management automatically, while C++ requires manual memory control.
Java is the better choice for kids learning programming. C++ is typically learned later in computer science education when students understand lower-level programming concepts.
Essential Java Concepts Kids Need to Know
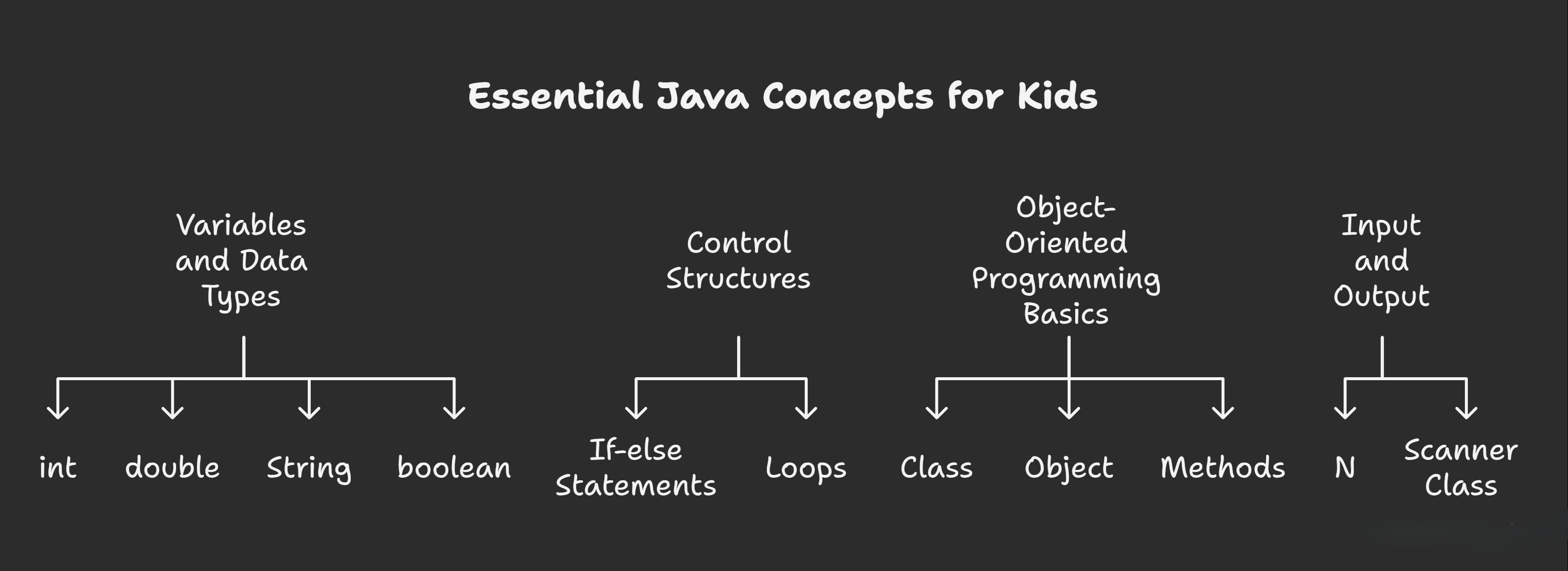
Variables and Data Types
Variables store information your program needs to remember. In Java, you must declare what type of data each variable holds.
Common data types:
- int: Whole numbers (age, score, count)
- double: Decimal numbers (price, temperature, distance)
- String: Text ("Hello", "Player Name")
- boolean: True or false values
Example:
int age = 12;
String name = "Emma";
double score = 95.5;Control Structures
If-else statements make decisions:
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("Great job!");
} else {
System.out.println("Keep practicing!");
}Loops repeat actions:
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Count: " + i);
}Object-Oriented Programming Basics
Think of a class as a blueprint. If you're building cars, the blueprint shows what every car needs: wheels, engine, doors, color.
An object is an actual car built from that blueprint. You can create many car objects from one car blueprint, each with different colors and features.
Methods are actions objects can perform. A car object might have methods like start(), accelerate(), and brake().
This way of organizing code makes large programs easier to understand and maintain.
Input and Output
Programs need to communicate with users. Java uses System.out.println() to display messages and the Scanner class to read user input.
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter your name: ");
String name = input.nextLine();
System.out.println("Hello, " + name + "!");Best Resources to Learn Java for Kids
Free Online Platforms
CodingBat (codingbat.com) Practice problems focusing on logic and problem-solving. Excellent for building Java skills through repetition.
Codecademy (codecademy.com) Interactive Java course with hands-on exercises. Free basic access with coding environment included.
Code.org (code.org) While focused on younger learners, offers foundational concepts that support Java learning.
YouTube Channels for Java Learning
- Programming with Mosh: Clear explanations perfect for beginners. Covers Java fundamentals thoroughly.
- Coding with John: Beginner-friendly tutorials with practical examples and projects.
- Telusko: Comprehensive Java tutorials from basics to advanced concepts.
Books for Kids Learning Java
"Java for Kids" by Yakov Fain: Specifically written for young learners. Uses games and projects to teach concepts.
"Head First Java": Visual approach with lots of diagrams and examples. Makes complex concepts easier to grasp.
"Java Programming for Kids" by R. Chandler Thompson: Step-by-step guide designed for middle school students.
These books explain Java without assuming prior programming knowledge, making them accessible for young beginners.
How to Set Up Java for Kids (Simple Steps)
Installing Java Development Kit (JDK)
The JDK contains everything needed to write and run Java programs. Download it from Oracle's website or use OpenJDK (open-source version).
Installation steps:
- Visit the official Java download page
- Choose the latest LTS (Long Term Support) version
- Download the installer for your operating system
- Run the installer and follow the prompts
- Verify installation by opening command prompt and typing java -version
Choosing a Beginner-Friendly IDE
An IDE (Integrated Development Environment) is software that helps you write and test code.
BlueJ: Designed specifically for beginners learning Java. Simple interface with visual class diagrams. Best starting point for kids.
Eclipse: Professional IDE with excellent free version. More features but steeper learning curve.
IntelliJ IDEA: Modern, powerful IDE with community edition. Great once kids are comfortable with Java basics.
Recommendation: Start with BlueJ for the first few months. Its simplified interface focuses on learning without overwhelming beginners with features.
Writing Your First Java Program
Every Java programmer starts with "Hello World":
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}What each line means:
- public class HelloWorld: Creates a blueprint named HelloWorld
- public static void main: The starting point where the program begins
- System.out.println: Prints a message to the screen
- The semicolon ends each statement
9 Fun Java Projects for Kids to Build
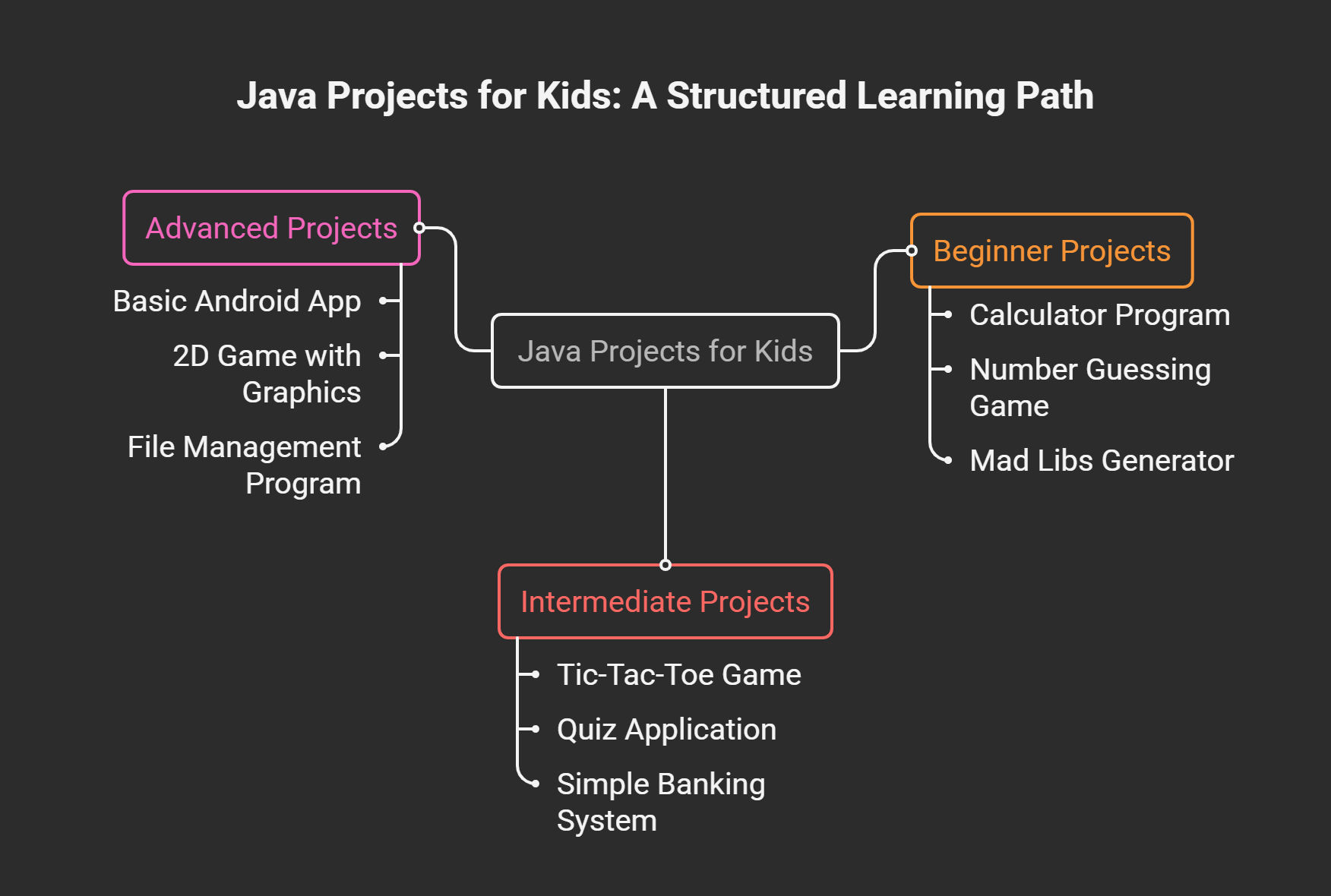
Beginner Projects (First Month)
Calculator program: Add, subtract, multiply, and divide two numbers based on user input.
Number guessing game: Computer picks a random number. User guesses until they get it right. Program gives "higher" or "lower" hints.
Mad Libs generator: Program asks for nouns, verbs, and adjectives, then creates a funny story.
Intermediate Projects (3-6 Months)
Tic-Tac-Toe game: Two players take turns. Program checks for winners and prevents invalid moves.
Quiz application: Ask multiple-choice questions, track score, display results at the end.
Simple banking system: Create accounts, deposit money, withdraw money, check balance.
Advanced Projects (6+ Months)
Basic Android app: Simple calculator or note-taking app for Android devices.
2D game with graphics: Use Java Swing to create games with moving characters and collision detection.
File management program: Read and write data to files, create a simple database system.
These projects teach Java concepts while creating something tangible kids can share with friends and family.
Java Programming Classes for Kids
What to Look for in Java Classes
Small class sizes: 5-6 students maximum ensures individual attention when kids get stuck.
Project-based learning: Building real applications teaches more than watching lectures.
Experienced instructors: Teachers who understand both Java and how kids learn make complex concepts accessible.
Structured curriculum: Clear progression from basics to advanced topics prevents confusion.
Types of Java Learning Programs
Live online classes provide real-time interaction with instructors and peers. Kids can ask questions immediately and get personalized feedback.
Self-paced video courses offer flexibility but require more self-discipline. Best for motivated learners who manage time well.
Coding camps provide intensive learning during school breaks. Kids dive deep into Java over one or two weeks.
For students aged 12-21 seeking structured Java education, Modern Age Coders offers project-based learning in small batches. Students build real applications while mastering Java fundamentals, with both weekend and weekday batch options available.
Tips for Parents Supporting Young Java Learners
Creating a Learning Environment
Set up a quiet coding space with minimal distractions. Good lighting and comfortable seating help kids focus during longer coding sessions.
Establish a regular practice schedule. Three 45-minute sessions per week work better than one long marathon session. Consistency builds skills faster than intensity.
Balance screen time appropriately. Coding is educational screen time, but kids still need breaks every 45-60 minutes to rest their eyes and move around.
Supporting Without Technical Knowledge
You don't need to know Java to help your child succeed. Ask them to explain what their program does. This reinforces their understanding and helps identify gaps in knowledge.
Learn alongside them. Many parents find that going through tutorials with their child creates bonding time and shows that learning is lifelong.
Celebrate small victories. Successfully running a program, fixing a difficult bug, or completing a project deserves recognition and encouragement.
When to Get Professional Help
Consider structured classes when your child feels stuck repeatedly, wants feedback on their code, or needs guidance on what to learn next.
Professional instruction becomes valuable when preparing for AP Computer Science or when kids want to build complex projects beyond tutorial scope.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Syntax Errors and Debugging
Java is case-sensitive. String works but string causes errors. Missing semicolons, unmatched brackets, and spelling mistakes are common beginner issues.
Solution: Use an IDE with syntax highlighting. It colors code differently based on what it is, making errors easier to spot. Read error messages carefully—they often point directly to the problem.
Understanding Object-Oriented Concepts
Classes and objects can feel abstract initially. Use real-world analogies that kids understand.
Example: A "Dog" class is a blueprint describing all dogs (they have names, breeds, and can bark). Creating a Dog object named "Buddy" who is a "Golden Retriever" makes it concrete.
Draw diagrams showing relationships between classes. Visual representations help kids grasp how objects interact.
Staying Motivated
Build projects based on your child's interests. A kid interested in sports might create a score-tracking app. An artist might build a digital drawing tool.
Join online coding communities for young programmers. Sharing projects and seeing what peers create maintains enthusiasm.
Participate in coding challenges appropriate for skill level. Small competitions provide goals and celebrate progress.
Java Career Opportunities Kids Should Know About
Learning Java early opens doors to exciting technology careers. Software developers create applications people use daily.
Android developers build mobile apps downloaded millions of times. Game developers bring interactive experiences to life.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects strong growth in software development careers through 2030.
Entry-level developers often start above $60,000 annually, with experienced developers earning $100,000-$150,000 or more.
But career prospects aside, Java teaches problem-solving, logical thinking, and persistence—skills valuable in any profession.
Whether your child becomes a programmer or pursues a different path, Java provides mental tools that translate across fields.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Java harder than Python for kids?
Yes, Java has a steeper learning curve than Python due to more complex syntax and strict rules. However, this structure teaches good programming habits. Kids comfortable with Python can transition to Java successfully with proper guidance.
Can a 10-year-old learn Java?
Some 10-year-olds can learn Java, especially if they have prior coding experience. However, most kids find it easier to start at 11-12 when their abstract thinking is more developed. Focus on readiness rather than age alone.
How long does it take to learn Java?
Basic proficiency takes 6-12 months with regular practice. Understanding core concepts and building simple projects might take 3-4 months. Becoming truly comfortable with Java and its ecosystem often takes 1-2 years of consistent learning.
Do kids need math skills for Java?
Basic arithmetic helps, but advanced math isn't required initially. Java uses math for certain programs (games with physics, data analysis), but many projects need only addition, subtraction, and basic logic. Problem-solving ability matters more than mathematical knowledge.
Is Java still relevant in 2026?
Absolutely. Java remains one of the top three programming languages globally. It powers millions of Android devices, enterprise applications, and web services. While new languages emerge, Java's stability and widespread use ensure it stays relevant for years to come.
Final Thoughts
Java provides kids with a powerful foundation in programming that prepares them for advanced computer science concepts and real-world applications. While it requires more dedication than visual programming languages, the skills gained through Java are invaluable for academic success and future careers.
Start with the basics, choose age-appropriate resources, and let your child build projects they're passionate about. Whether it's creating games, developing Android apps, or preparing for AP Computer Science, Java offers countless opportunities for young coders.
For students aged 12-21 ready to learn Java seriously, Modern Age Coders offers project-based Java education where you build real applications while mastering programming fundamentals through hands-on learning.
Remember: every expert programmer started as a beginner. With patience, practice, and the right guidance, your child can master Java and open doors to exciting possibilities in technology. The journey begins with a single line of code—and that first step starts today.
