Table of Contents
- What is Coding for Kids? Understanding the Basics
- Why Coding is Important for Kids in Today's Digital World
- Essential Coding Concepts For Kids
- Best Programming Languages for Kids by Age
- Top Coding Platforms and Apps for Kids
- Best Coding Books for Kids to Learn Programming
- Coding Classes for Kids: What to Expect
- Free Coding Resources and Activities for Kids
- How Parents Can Support Young Coders
- Common Questions About Coding for Kids
- Getting Started: Your First Steps
- Final Thoughts
You've probably heard the buzz about kids learning to code, but what does "coding for kids" actually mean? Is it just another educational trend, or is there real value in teaching young children to program computers?
Here's the truth: coding for kids isn't about turning every child into a software engineer. It's about giving them tools to think logically, solve problems creatively, and understand the technology that shapes their world. And the best part? Kids as young as four can start grasping basic coding concepts—no reading required.
What is Coding for Kids? Understanding the Basics
Coding is the process of giving step-by-step instructions to a computer to make it perform specific tasks. Think of it like writing a recipe—you tell the computer exactly what to do, in what order, so it can complete a task successfully.
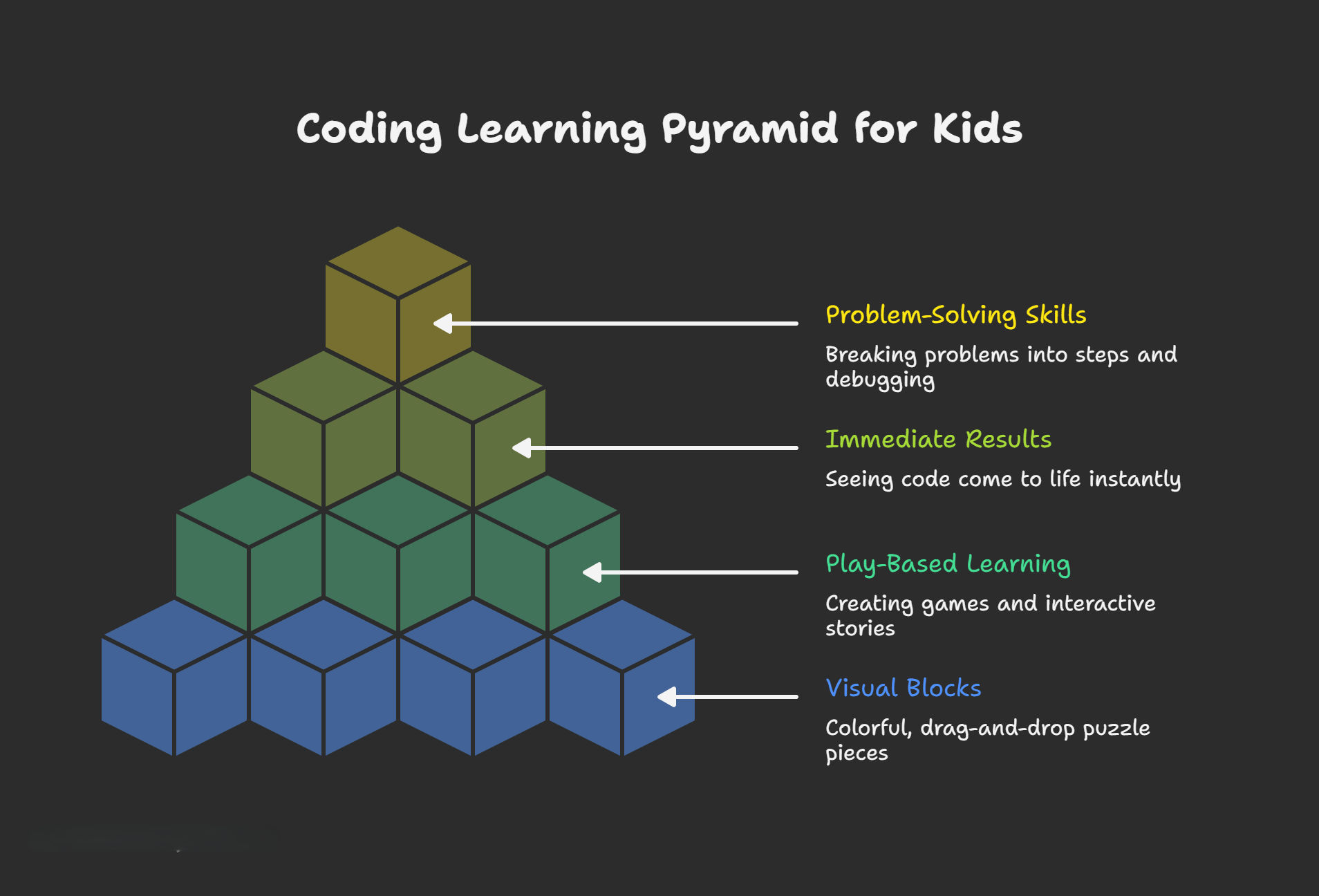
How kids learn coding differently from adults:
- Visual blocks vs. text: Professional programmers write lines of code in languages like Python or JavaScript. Kids start with colorful, drag-and-drop blocks that snap together like puzzle pieces.
- Play-based learning: Young coders create games, animations, and interactive stories rather than building complex software applications.
- Immediate results: Kids see their code come to life instantly—a character moves, a sound plays, or a game level starts.
A five-year-old using Scratch Jr. drags blocks to make a cartoon character dance across the screen. An eight-year-old creates a maze game where players collect points and avoid obstacles. A twelve-year-old writes Python code to build a chatbot that answers questions.
The real value isn't in memorizing commands or syntax. It's in how kids learn to think—breaking problems into steps, debugging errors patiently, and creating something from nothing.
Why Coding is Important for Kids in Today's Digital World
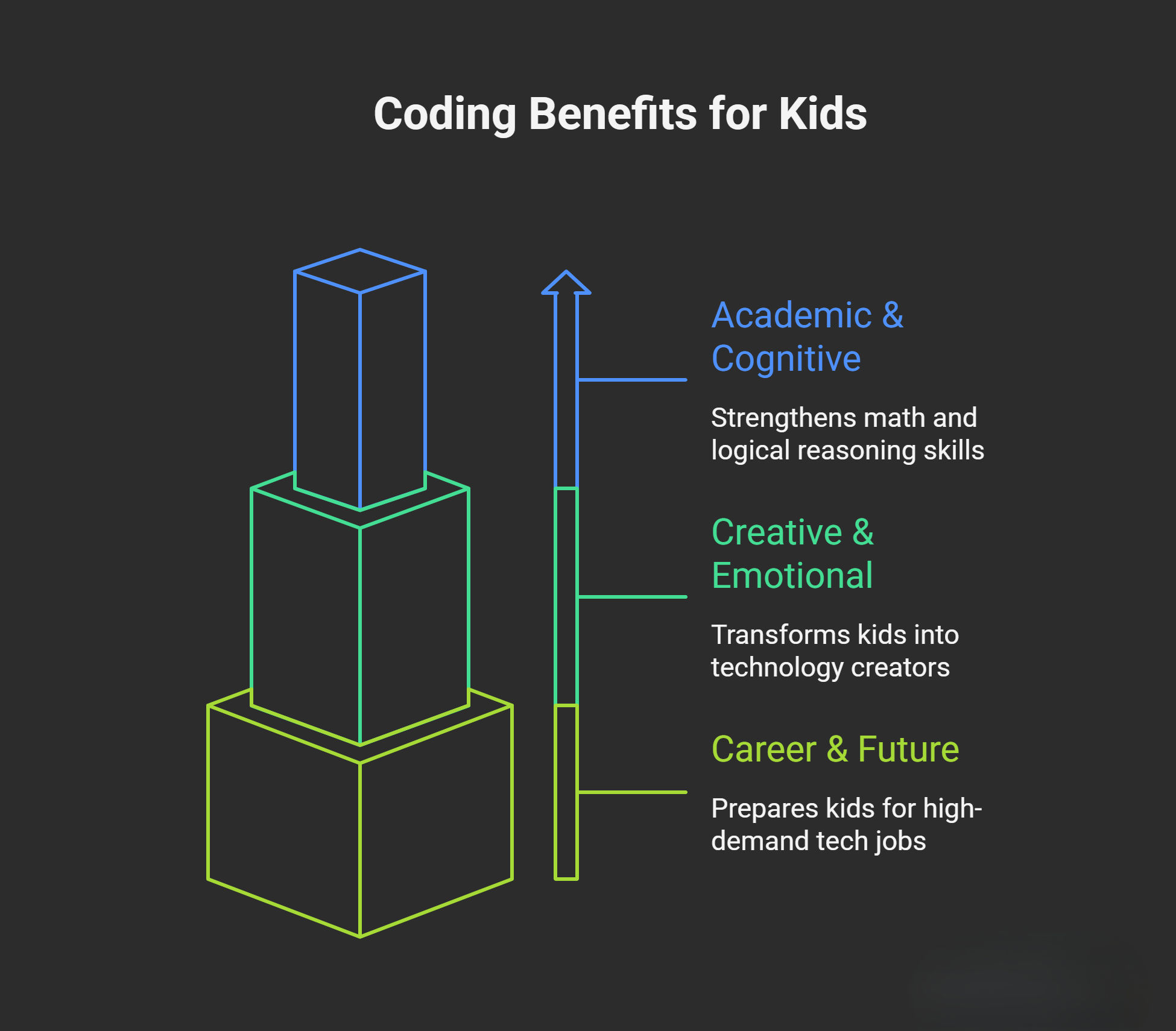
Academic and cognitive benefits:
- Strengthens math skills: Coding uses logic, patterns, and spatial reasoning that directly support mathematical thinking and computational skills.
- Improves problem-solving: Kids learn to break complex challenges into manageable steps through algorithmic thinking.
- Builds logical reasoning: Programming requires cause-and-effect thinking that transfers to science, reading comprehension, and everyday decisions.
Creative and emotional development:
Coding transforms kids from technology consumers into creators. Instead of just playing games, they design their own. Instead of watching animations, they build interactive stories.
This shift builds genuine confidence. When a child says "I made this" and shows you a working game or animation, they've proven to themselves that they can create something meaningful.
The debugging process teaches resilience. Every coder deals with errors and bugs—it's not about avoiding mistakes, but learning to fix them systematically through patience and persistence.
Career and future readiness:
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, technology occupations had a median annual wage of $91,250 as of May 2020, with employment projected to grow 11% between 2019 and 2029. Understanding how computers "think" helps kids navigate a digital world more safely and effectively.
Essential Coding Concepts For Kids
Here's what surprises parents: four-year-olds can understand coding concepts before they learn to read. The foundations of programming are really just structured ways of thinking that children use naturally.
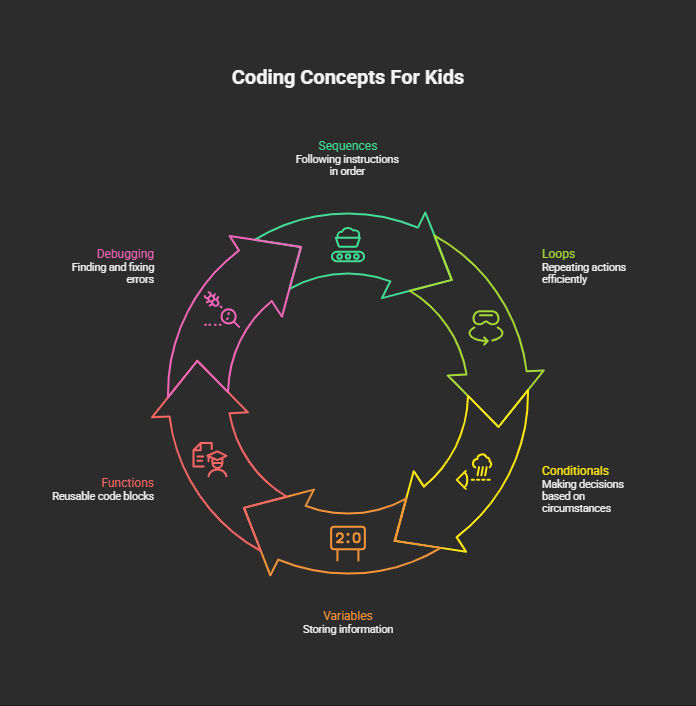
Sequences: Following Steps in Order
A sequence is a set of instructions that must happen in a specific order. Making a sandwich requires a sequence: get the bread, spread peanut butter, add jelly, close the sandwich.
In coding, sequences work identically. To make a character walk across a screen, you sequence commands: move right, move right, move right, stop.
Loops: Repeating Actions Efficiently
Loops tell the computer to repeat an action multiple times. When brushing teeth, kids repeat the motion automatically without thinking about each stroke.
In coding, if you want a character to bounce five times, you write "bounce" once and tell it to loop five times.
Conditional Statements: If-Then Logic
Conditionals let programs make decisions based on circumstances. Kids make these decisions constantly: "If it's raining, I'll play inside. If it's sunny, I'll go to the park."
In coding: "If the character touches a wall, turn around. If the character reaches the goal, play victory music."
Variables: Storing Information
Variables act as containers that hold information. Imagine a box labeled "score" that keeps track of points in a game, or a container called "name" that stores a player's username.
Functions: Reusable Code Blocks
Functions group related commands together so you can reuse them. Getting ready for school is a function containing smaller tasks: brush teeth, get dressed, eat breakfast.
In coding, you create a "jump" function once, then call it whenever needed instead of rewriting the same commands repeatedly.
Debugging: Finding and Fixing Errors
Debugging means identifying mistakes and correcting them. When reading a story and encountering a sentence that doesn't make sense, kids naturally go back to figure out what went wrong.
Professional programmers spend significant time debugging. Teaching kids this skill early builds problem-solving resilience.
Best Programming Languages for Kids by Age
Different programming languages suit different age groups and skill levels. Here's what works best at each stage.

Ages 5-7: Block-Based Visual Programming
- Scratch Jr.: Designed specifically for young learners, using visual blocks with no text required. Kids create animations and interactive stories.
- Blockly: Google's visual programming language that appears in many educational apps and games.
Ages 8-12: Transitional Languages
- Scratch: MIT's full platform for creating games, animations, and interactive projects with more complexity than Scratch Jr.
- Python: Simple syntax makes it ideal for beginners. Kids can create games, calculators, and simple programs with readable, English-like commands.
Ages 13+: Professional Languages
- JavaScript: Powers interactive websites and web applications. Essential for aspiring web developers.
- Java: Used for Android app development and widely taught in computer science courses.
- HTML/CSS: Not programming languages but essential for building websites. Great gateway to web development.
- C++: More advanced language for game development and systems programming.
Top Coding Platforms and Apps for Kids
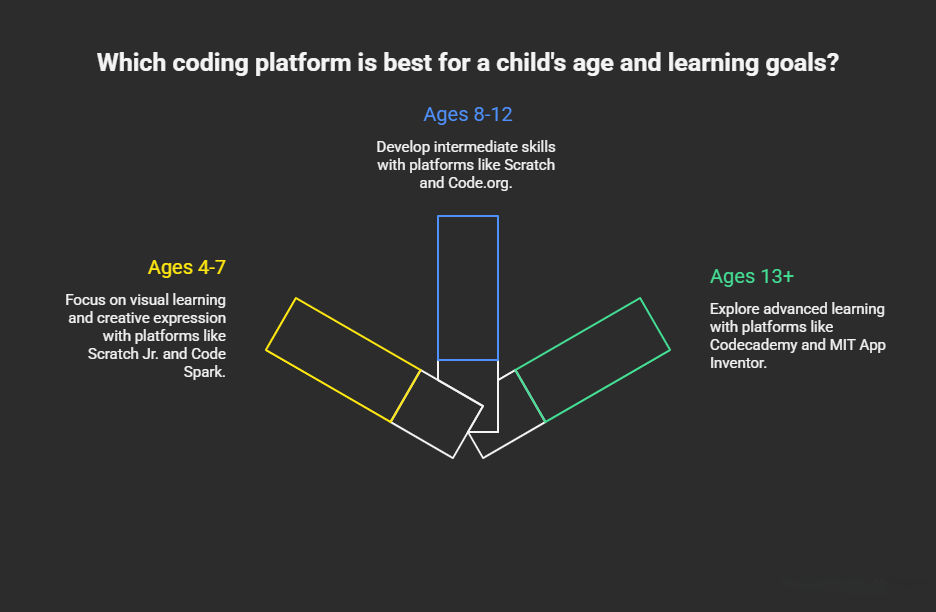
For Ages 4-7: Visual Learning
Scratch Jr.
Platform: iOS, Android, free
Website: scratchjr.org
Best for: Storytelling and creative expression
Code Spark
Platform: iOS, Android, web
Website: codespark.com
Cost: 7-day free trial, $7.99/month
Best for: Gamified learning
Kodable
Platform: iOS, web
Website: kodable.com
Cost: Free trial, $6.99/month
Best for: Maze-based logic puzzles
For Ages 8-12: Intermediate Skills
Scratch
Platform: Web browser, free
Website: scratch.mit.edu
Best for: Creative projects and game development
Code.org
Platform: Web browser, free
Website: code.org
Best for: Structured curriculum by grade level
Khan Academy
Platform: Web browser, free
Website: khanacademy.org
Best for: JavaScript, HTML, CSS tutorials
For Ages 13+: Advanced Learning
Codecademy
Platform: Web browser
Website: codecademy.com
Cost: Free basic, $16+/month Pro
Best for: Professional programming languages
MIT App Inventor
Platform: Web browser, free
Website: appinventor.mit.edu
Best for: Android app development
Best Coding Books for Kids to Learn Programming
Books provide screen-free learning and reference materials that complement online coding practice. Here are top recommendations by age group.
Ages 4-7: Introduction Through Stories
"Hello Ruby: Adventures in Coding" by Linda Liukas Introduces computational thinking through storytelling without requiring screens. Ruby solves problems using logic and creative thinking.
"How to Code a Sandcastle" by Josh Funk Uses beach building to teach programming concepts like sequences and loops in relatable ways.
"My First Coding Book" by Kiki Prottsman Interactive book with flaps and wheels that teach coding fundamentals through hands-on activities.
Ages 8-12: Project-Based Learning
"Coding Games in Scratch" by DK Step-by-step visual instructions for creating games. Kids learn by building actual projects they can play.
"Python for Kids" by Jason Briggs Accessible introduction to text-based programming with fun projects like games and animations.
"Get Coding!" by Young Rewired State Adventure story where kids learn HTML, CSS, and JavaScript by solving coding missions.
"Girls Who Code: Learn to Code and Change the World" Inspiring introduction with practical projects designed to encourage all kids, especially girls, to explore coding.
Ages 13+: Advanced Concepts
"JavaScript for Kids" by Nick Morgan Professional language taught through playful projects. No prior experience needed.
"Automate the Boring Stuff with Python" by Al Sweigart Practical applications showing how coding solves real-world problems. Great for teens who want to see coding's usefulness.
"Coding for Teens" by Jeremy Moritz Comprehensive guide covering web development, app creation, and game design for teenage learners.
"Head First Programming" by Paul Barry Visual, engaging approach to learning programming fundamentals with lots of examples and exercises.
Coding Classes for Kids: What to Expect
Structured coding classes provide curriculum, instruction, and peer learning that self-paced apps can't match.
What Coding Classes Teach
Technical skills:
- Programming language syntax and structure
- Problem-solving through algorithmic thinking
- Debugging techniques and error handling
- Project planning and execution
Soft skills:
- Collaboration and teamwork on group projects
- Persistence when facing challenges
- Creative thinking and innovation
- Presentation and communication skills
Types of Coding Programs
- Online classes: Live instruction via video with small groups. Students code alongside instructors and get real-time feedback.
- In-person workshops: Local classes at libraries, community centers, or coding schools. Hands-on learning with face-to-face instruction.
- Summer coding camps: Intensive programs during school breaks. Kids dive deep into specific topics over one or two weeks.
- After-school programs: Regular sessions during the school year. Consistent practice builds skills progressively.
- Self-paced courses: Video tutorials and exercises students complete independently. Good for motivated learners who prefer flexible timing.
For students aged 12-21 seeking serious coding education, programs like Modern Age Coders teach professional languages (Python, JavaScript, Java, C++) through project-based learning in small batches.
Free Coding Resources and Activities for Kids
Free Online Platforms
Code.org: Hour-long tutorials organized by grade level from kindergarten through high school.
Khan Academy: Video instruction plus practice exercises covering JavaScript, HTML, CSS, and computer science principles.
Scratch Community: Browse millions of projects created by other kids, remix existing work, and share your own creations.
Unplugged Coding Activities For Kids
Robot commands: One child acts as a robot while another gives precise step-by-step instructions to navigate obstacles.
Algorithm hopscotch: Create a hopscotch grid and have kids write the "code" (sequence of jumps) before executing it.
Binary bracelets: Make bracelets using different colored beads to represent binary code, teaching how computers store information.
Debugging treasure hunts: Write intentionally incorrect instructions for finding treasure, then debug the sequence together.
These activities teach computational thinking without screens—perfect for balancing digital and physical learning.
YouTube Channels for Learning to Code
Code.org: Official channel with tutorials and inspiring stories from tech professionals.
Tynker: Project tutorials and coding challenges for different skill levels.
Kodable: Short videos explaining coding concepts with kid-friendly examples.
How Parents Can Support Young Coders
You Don't Need Technical Knowledge
Your child doesn't need you to know programming—they need you to show interest. Ask them to explain what they're building. Show genuine curiosity about how their code works.
When you learn together, you model that adults don't know everything, and that's perfectly acceptable.
Create a Learning Environment
Dedicated space: Quiet corner with minimal distractions, comfortable seating, and good lighting.
Regular schedule: Set aside 2-3 times weekly for coding practice. Consistency builds skills faster than occasional marathons.
Balance screen time: Distinguish educational coding from passive entertainment. Set time limits even for learning activities.
Encourage and Celebrate Progress
Praise problem-solving efforts, not just finished projects. Point out when they debug effectively or think creatively. Share their creations with family members who can appreciate their work.
Small, consistent recognition builds the confidence kids need to tackle increasingly difficult challenges.
Connect Coding to Their Interests
Kids stay motivated when coding connects to things they already love. Sports fans can create score-tracking apps. Artists can explore generative art. Music lovers can program rhythm games.
Common Questions About Coding for Kids
What age should kids start coding?
Children as young as four can begin with visual, block-based platforms. If your child can follow simple instructions and enjoys puzzles, they're ready to explore introductory activities.
Is coding good for my child's brain development?
Yes. Coding strengthens logical reasoning, pattern recognition, spatial awareness, and executive function skills. These cognitive benefits transfer to academic performance across subjects.
How long does it take to learn coding?
Basic concepts: 3-6 months of regular practice. Intermediate skills: 6-12 months. Proficiency in a specific language: 1-2 years. Coding is an ongoing learning journey rather than a destination.
Can coding help with school subjects?
Absolutely. Coding improves math performance through applied logic. It enhances writing through algorithmic thinking. It supports science through computational modeling and data analysis.
Getting Started: Your First Steps
Week 1: Talk with your child about what they'd like to create. Try one free platform like Code.org or Scratch together.
Week 2: Download age-appropriate apps or visit free websites. Let your child explore without pressure. Observe which platform holds their attention.
Week 3: Set aside 2-3 times weekly for coding. Start with 20-30 minute sessions in a dedicated space.
Week 4: Evaluate engagement. Are they asking to code independently? Consider books or structured classes if they want more depth.
Final Thoughts
Coding for kids teaches logical thinking, creative problem-solving, and digital literacy—skills valuable in any career path. Start small, keep it fun, and remember that every programmer once wrote their first "Hello World."
The future is built with code, and your child can be part of creating it.


